The Neogene Period spans 22 million years, during which the world became much drier and cooler, culminating in the biotic disaster of the Pleistocene ice age and the harsh conditions of today. The Neogene is divided into 4 epochs: the Miocene, Pliocene, Pleistocene, and the Holocene. We will now describe each epochs climate and we shall begin with the Miocene.
The Miocene was a time of warmer global climates than those in the preceding Oligocene, or the following Pliocene. During this time modern patterns of atmospheric and ocean circulation formed. The isolation of Antarctica from Australia and South America significantly reduced the mixing of warmer tropical water and cold polar water, and further led to the buildup of the Antarctic ice cap.
The Pliocene saw the continuation of the climatic cooling that had began in the Miocene, with the beginning of the large ice caps, especially in Antarctica, and the northern hemisphere lands and ocean cooling as-well. Antarctica was not yet completely frozen. Throughout the Pliocene climates became cooler and drier, and seasonal, similar to modern climates. Ice sheets grew on Antarctica during the Pliocene. Mid-latitude glaciation was probably underway before the end of the epoch. It is believed that the global cooling that occurred during the Pliocene may have spurred on the disappearance of forests and the spread of grasslands and savannas.
Then, about a third of the way into the Pleistocene, the first Ice Age hit. There were a series of advances and retreats of the ice, as the climate fluctuated between cold and warm periods. The sea level rose during the melting of the glaciers, then dropped again during the next long cold spell. The lowered sea levels formed land bridges that enabled the migration of animals and humans across continents. Pleistocene climate was characterized by repeated glacial cycles where continental glaciers pushed to many places. It is estimated that 30% of the Earth's surface was covered by ice. The effects of glaciation were global.
Now onto our final Epoch, the Holocene. Although geographic shifts in the Holocene were minor, climatic shifts were very large. Ice core records show that before the Holocene there were global warming and cooling periods, but climate changes became more regional. However, the maximum warmth flowed south to north from 11,000 to 7,000 years ago. It appears that this was influenced by the residual glacial ice remaining in the Northern Hemisphere until the latter date. This so called "hypsithermal" was a period of warming in which the global climate became 33 to 36°F warmer than today. However, the warming was probably not uniform across the world. This period ended about 5,500 years ago, when the earliest human civilizations in Asia and Africa were flourishing. This period of warmth ended with the descent into the Neoglacial. At that time, the climate was not unlike today's, but there was a slightly warmer period from the 10th–14th centuries known as the Medieval Warm Period. This was followed by the Little Ice Age, from the 13th or 14th century to the mid 19th century, which was a period of significant cooling, though not everywhere as severe as previous times during neoglaciation.
In Summary, climates cooled somewhat over the duration of the Neogene, culminating in continental glaciations in the Quaternary sub-era or period, in some time scales that follows, and that saw the dawn of the genus Homo.
martes, 30 de septiembre de 2008
lunes, 29 de septiembre de 2008
In this first Post, we shall give a brief introduction of our time period. The Neogene Period was a time of big changes for the earth. The climate became cooler and drier. Grasslands replaced forests. The animals had to adapt to these changing conditions or face extinction. It was also the period where Human civilization began and when the last Ice Age. The first humans (Homo sapiens) evolve, while all around them Mammoths, mastodons, saber-toothed cats, giant ground sloths, and other Pleistocene megafauna live. A mass extinction of large mammals and many birds happened about 10,000 years ago, probably caused by the end of the last ice age. First hominids (australopithecines). Modern forms of whales and Megalodon swam the seas. More mammals, including the horses, dogs and bears and modern birds. Truly, this period was, and still is, filled with great change and excitement. Our second post shall talk about our first topic, which is the climate of the Neogene Era.
Suscribirse a:
Entradas (Atom)
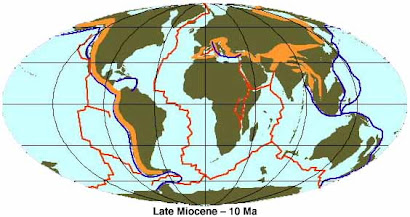
The Neogene
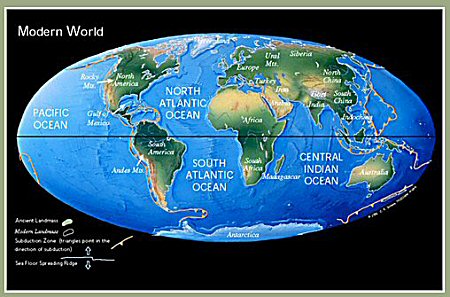
The Present
Referncias de la Investigacion
- http://palaeos.com/Cenozoic/Neogene.html
- http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/prehistoric-world/neogene.html
- http://www.fossils-facts-and-finds.com/neogene_period.html
- http://www.humboldt.edu/~natmus/Case_indexes/Neogene/Neogene.html
- http://www.humboldt.edu/~natmus/lifeThroughTime/Neogene.web/index.htm
